Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a powerful and flexible cloud computing platform, but like most cloud environments, the security settings out-of-the-box are usually not enough for a production environment. Organizations deploying AWS must take an active role in securing their environments to prevent misconfigurations and vulnerabilities. According to a Gartner survey, misconfiguration-related issues cause 80 percent of all security breaches. The AWS Shared Responsibility Model clarifies the division of security responsibilities between AWS and its customers, ensuring that organizations understand their role in maintaining a secure cloud infrastructure.
The AWS Shared Responsibility Model
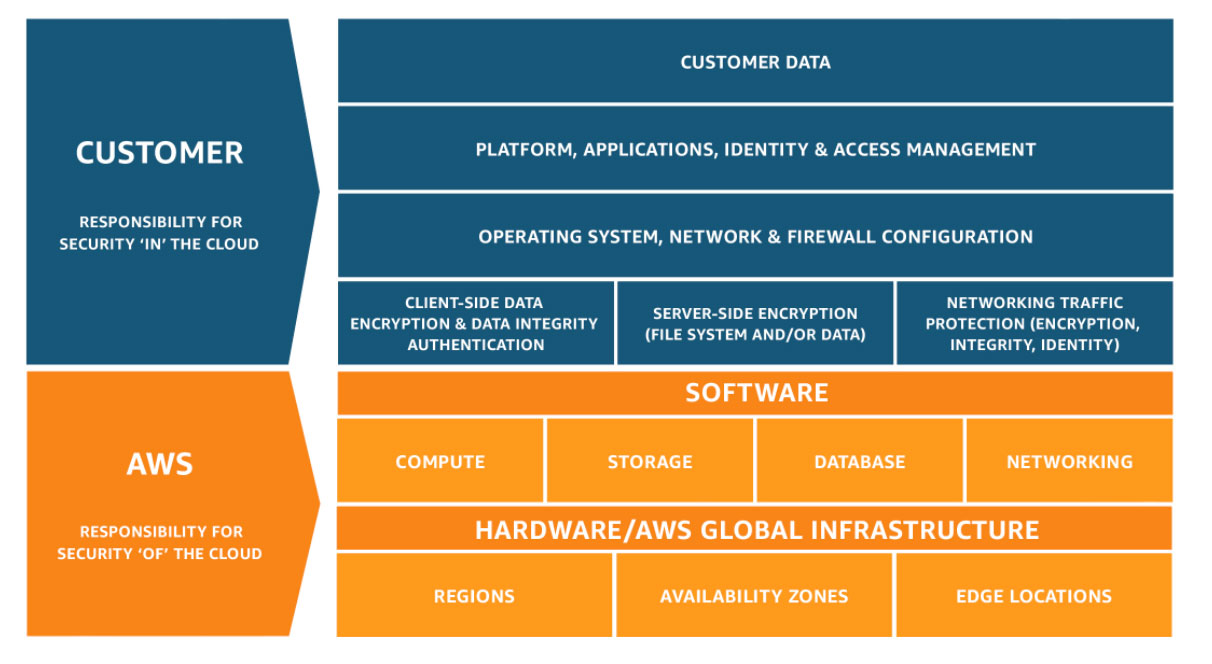
AWS operates under a Shared Responsibility Model, which delineates security responsibilities between AWS and its customers. AWS is responsible for securing the infrastructure that runs AWS Cloud Services, including hardware, software, networking, and data center facilities. Customers, on the other hand, are responsible for configuring and securing their cloud environments. This includes protecting customer data, securing applications and platforms, managing Identity and Access Management (IAM), implementing server-side encryption, and ensuring network traffic protection. Each AWS customer’s security responsibilities vary based on the AWS services they use, their integration with other services, and their regulatory compliance requirements. Properly understanding and implementing these responsibilities is critical for preventing security breaches.
The Risks of Misconfiguration
Customers must configure AWS environments themselves to achieve proper security, so there is a risk that misconfigurations will expose organizations to significant security risks. Without proper controls, companies may unknowingly leave their data and systems vulnerable. One example occurred last year when attackers targeted AWS customers by repurposing misconfigured Amazon S3 buckets, effectively using them as shared drives. Hackers accessed sensitive data, including exposed system endpoints, database credentials, and AWS keys. These stolen credentials were later exploited to gain deeper access into networks and achieve remote shell execution. The hackers also used the credentials as a bridge to begin sending fraudulent and phishing messages to gain admin privileges on Amazon SES email and SNS notification services.
Addressing Common Cloud Security Risks
To mitigate security risks, AWS customers must proactively secure their cloud environments. Some of the most common concerns and effective mitigations include:
- Root account security measures, such as ensuring accurate security contact details, enabling Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), and not using the root account for administrative or daily tasks to minimize security risks.
- IAM configuration, including structuring permissions with a unified management system, assigning IAM policies to user groups to ensure consistent permissions, and reducing the risk of excessive privileges.
- Insecure S3 buckets. By default, Amazon S3 allows HTTP and HTTPS access, but organizations must explicitly deny HTTP requests to enforce secure HTTPS-only access. Additionally, S3 buckets and objects can be unintentionally made public, increasing exposure to potential breaches. Using Block Public Access settings can help prevent unauthorized access.
- Insufficient logging and monitoring can lead to undetected security events, such as unauthorized access attempts. AWS CloudTrail should be enabled to record API calls and track resource changes, aiding in security analysis and anomaly detection. Another important security tool is AWS Security Hub, which aggregates security data from various AWS services and third-party integrations. This allows organizations to analyze security trends, identify high-priority threats, and strengthen their overall cloud security posture.
How a Third-Party Cloud Security Assessment Can Help
A proactive approach to AWS security is essential to prevent breaches and maintain compliance. Tangible Security specializes in helping organizations secure their AWS environments through Cloud Security Assessments. By reviewing cloud configurations against the latest CIS Benchmarks and security best practices, we identify misconfigurations and vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. Our assessments provide actionable recommendations to enhance security and achieve compliance. If you are looking to strengthen your AWS security posture, contact Tangible Security to learn how we can help protect your cloud environment.
Learn more: https://tangiblesecurity.com/cloud-security-assessment/



Recent Comments